.
Master of Technology (M. Tech.) in Power Electronics and Drives is a 2 year full time professional postgraduate course offered by Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering and was started in the year 2011. The program provides state-of-the-art training in Power Electronics, Converters, Machine drives, Renewable Energy Sources, Electric Vehicles, Power System related applications. It is an industry oriented program which encompasses the fields of Electrical Engineering and caters knowledge about analysis, design, integration and the operations of motor drives and machines. The curriculum structure and the well-equipped laboratories facilitate both the research needs of graduate students and the practical expertise to meet the challenges of the industry. Facilities include Microprocessors and Embedded Systems Lab, Power Electronics & Drives Lab, Electrical Machinery Lab, Power Systems Lab, Control systems lab, Computer lab Departmental Library. The research laboratory includes most modern D-Space controllers, DSTATCOM, Solar and wind emulators, Fuel Cell units, IGBT based inverter, FPGA and PWM cards, PLC training kit, TMS DSP kits and Simulation facilities with softwares like MATLAB, Lab VIEW, ANSYS, MiPower, PSCAD, etc. The department has links with industry and a well-connected alumni network. There are ample jobs after M.Tech Power Electronics and Drives that range in the private and public sectors. Some of the major companies where the Alumni of the course are placed includes ABB, L&T, Robert Bosch, Tata Elxsi, ………etc….
PO1: Technical Knowledge/ Degree of Mastery: An ability to demonstrate a degree of mastery in the field of power electronics and drives.
PO2: Design and Development: An ability to apply the knowledge aquired in Power Electronics and Drives to design and develop solutions for real world problems by following the standards.
PO3: Research Skills: An ability to independently carry out investigation, research and development work to propose creative and innovative solutions in power electronics and allied arena
PO4: Technical Communication Skills:An ability to communicate effectively, write and present technical reports on complex engineering activities by interacting with the engineering fraternity and with the society at large.
PO5: Modern Tool Usage: An ability to identify, select and apply appropriate techniques, resources and state-of-the-art tools to model, analyse and solve practical engineering problems.
PO6: Ethical Practice and Social Responsibility: An ability to adopt to life-long learning to innovate, modernise and to go in line with the technical progress in power electronics and allied areas, considering the sustainability, societal, ethical and environmental aspects.
PO7: Multidisciplinary Work and Management skills: Ability to work in a team of engineers/ researchers of various disciplines and specializations to take up multidisciplinary development projects involving managerial and financial challenges which may lead to Entrepreneurship and soluions viable to Industry.
PO8: Electrical Vehicles and Embedded Applications: (PSO1): Ability to appreciate the importance of advanced concepts in control, softwares, magnetics etc in the design, development and compact or embedded implementation of topologies and power control strategies to facilitate miniaturised and energy efficient solutions in power applications including Electrical Vehicles.
PO9: Alternative Energy Integration and Power Quality: (PSO2): Analyse, design and suggest new techniques to integrate various renewable energy sources to locally supply, or connect to the power grid to meet the increasing energy demand economically, efficiently and with improved power quality
PEO 1. Produce technically competent graduates in the field of power control and power electronics employable in public and private industries/ Institutes/Organizations, or can pursue a wide range of careers as consultants and entrepreneurs.
PEO 2. Identify and address current and to be known problems in the domain of renewable energy utilisation, power electronics and electrical drives and to develop feasible and viable solutions in an economic, social and environmental context.
PEO 3. Inculcate effective communication skills, practice effective team work, professional ethics and pursue research with commitment towards sustainable development.
The complete system was assembled in our lab using Semikron inverter module (three phase), LEM sensors (voltage and current measurement), 6N136 based gate drive, interfacing inductor and RC ripple filter. The system can operate as a DSTATCOM (providing power quality improvement) or as a renewable energy based inverter (active power injection + power quality improvement). The variety of local loads can be connected. (Non linear, RL, combined). The complete system is controlled using dSpace MicroLab Box. For the control purpose, Matlab/Simulink and Controldesk softwares are used.
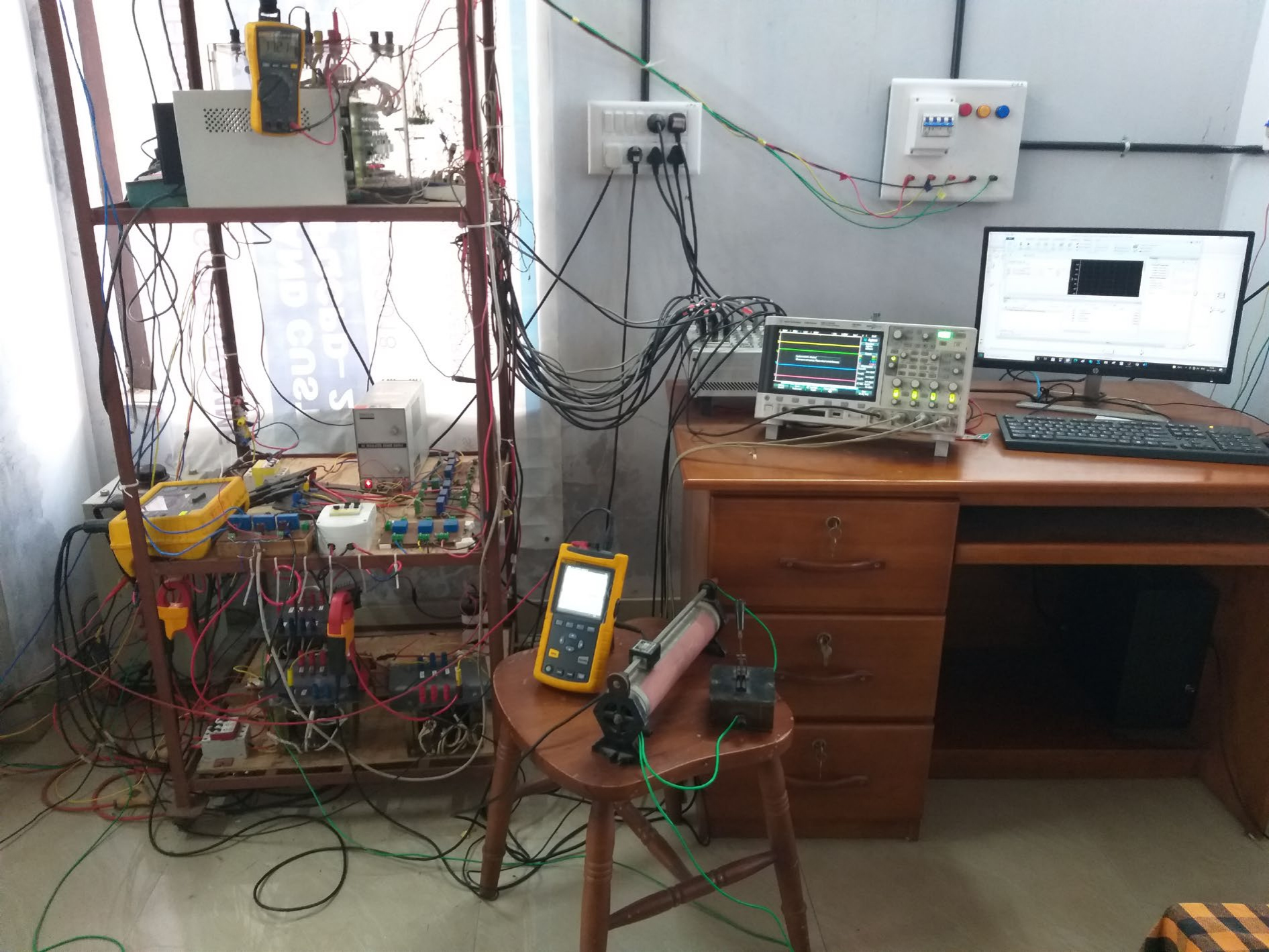

Photo of grid connected three phase inverter along with host PC, Power quality analyser and DSO
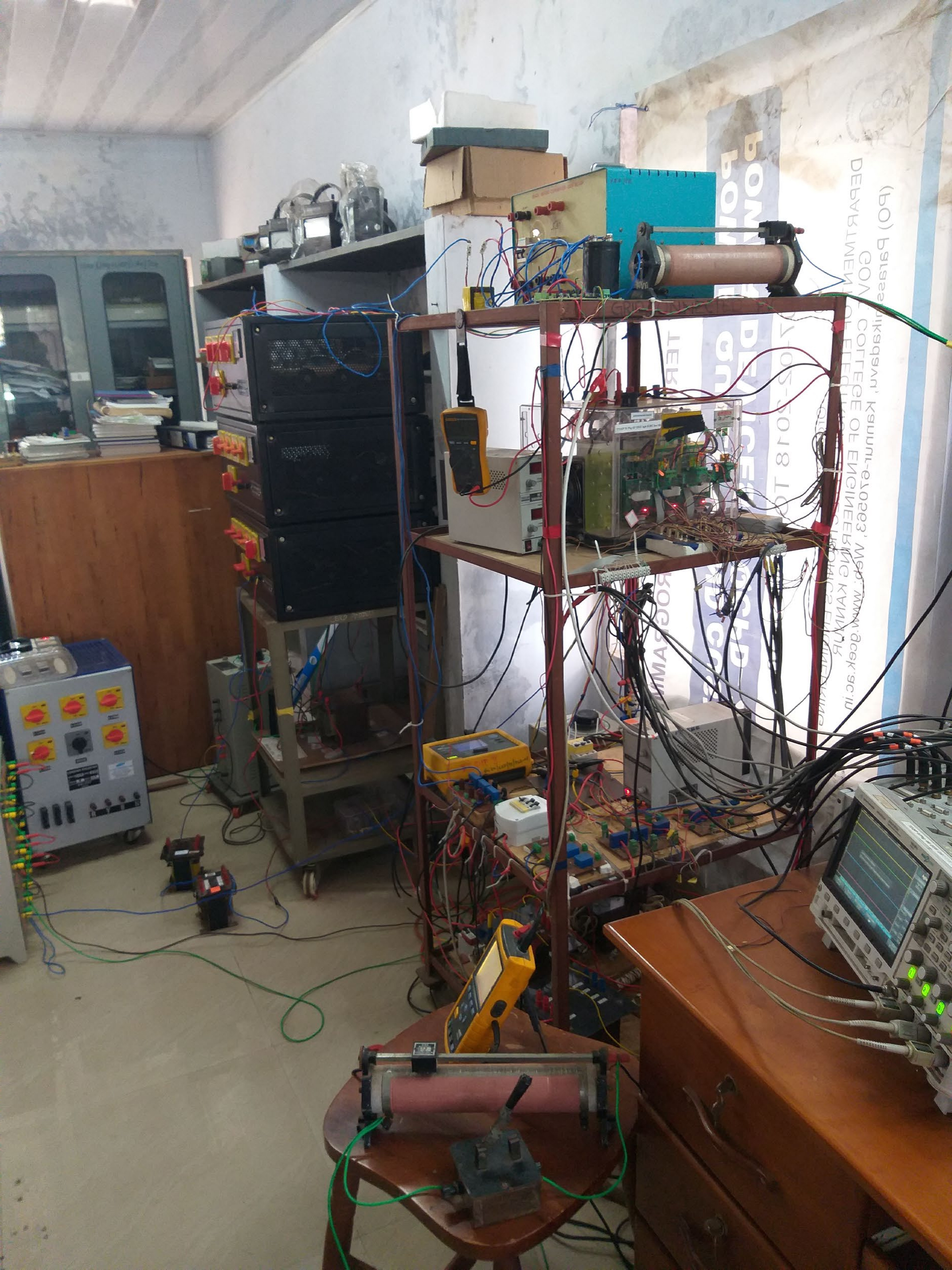

Grid connected three phase inverter with different loads
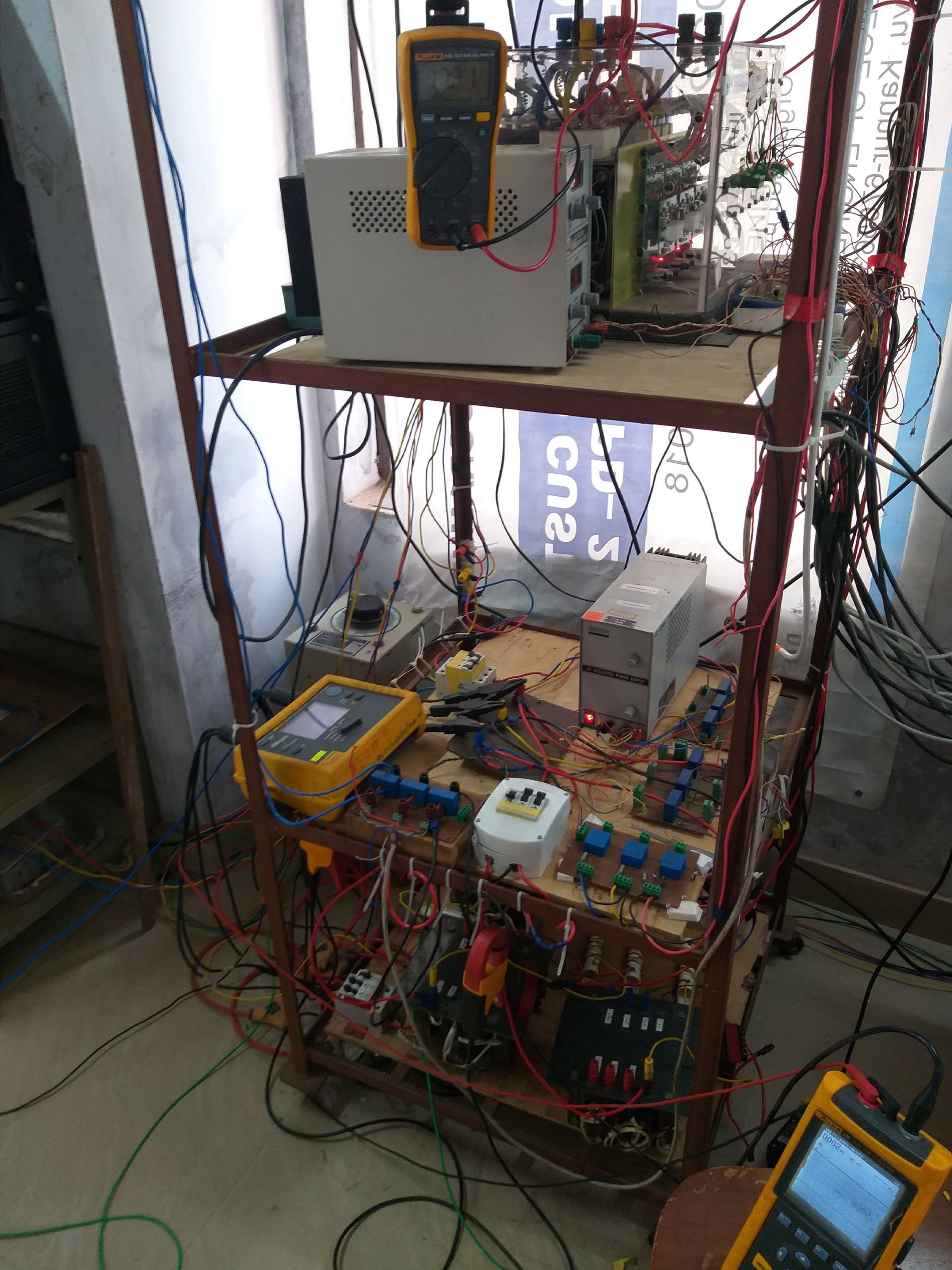

Grid connected three phase inverter – Semkron module and gate driver (top rack), LEM sensors (middle rack), Interfacing inductor and RC ripple filter (bottom rack)
This microgrid system consists of a wind turbine emulator, PV emulator and fuel cell as sources and a lithium ion battery for energy source. These sources are connected to a 120 B DC link through DC-DC converters. Then the system is connected to the grid through an inverter and transformer. The system is controlled using an FPGA based controller and LabVIEW software This system has been provided by Ecosense Sustainable Solutions Pvt. Ltd, Delhi.
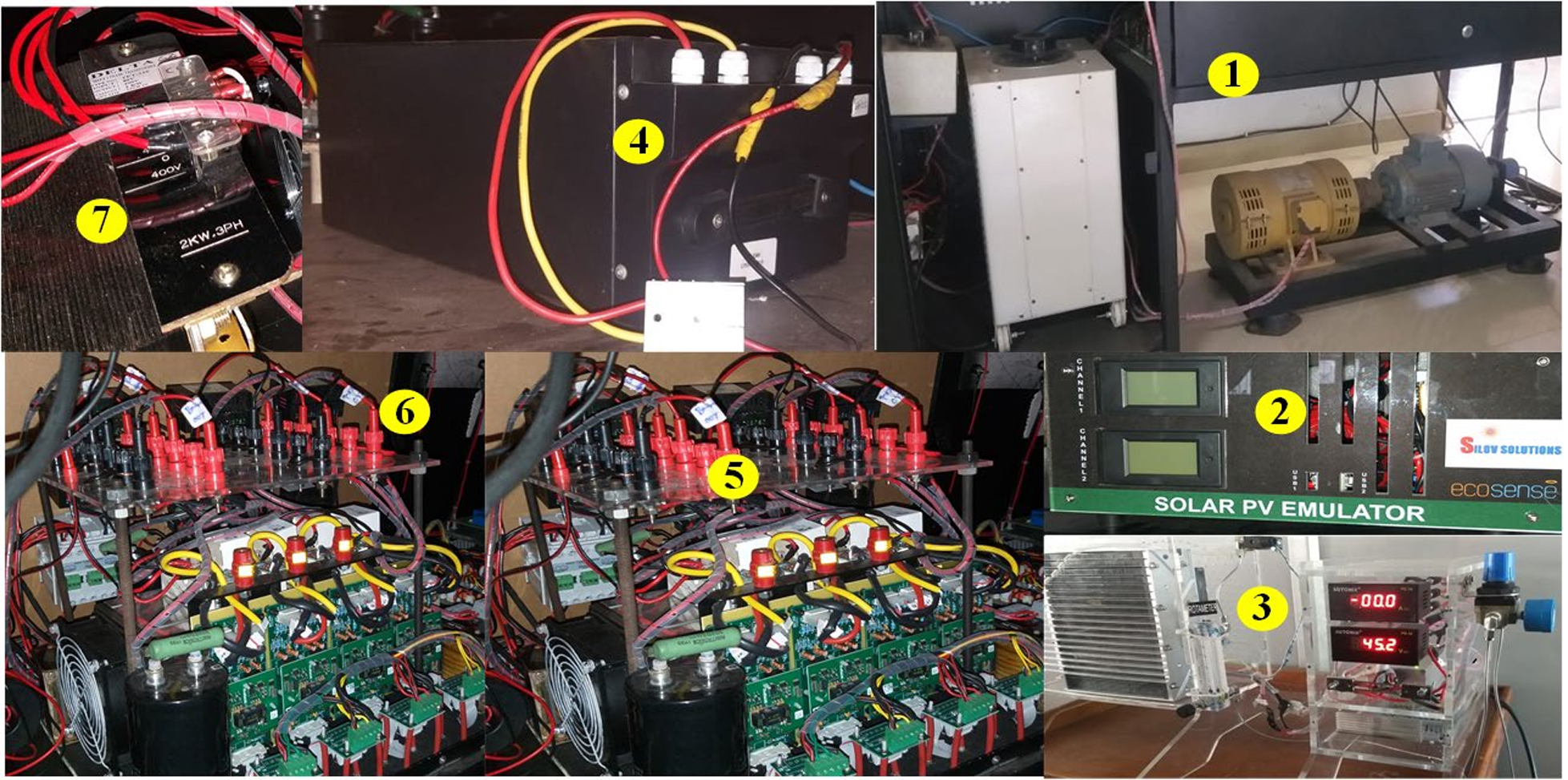
Components in the microgrid – 1. Wind turbineemulator 2. PV emulator 3. Fuel cell 4. Battery 5. DC-DC converters 6. Inverter 7. Transformer
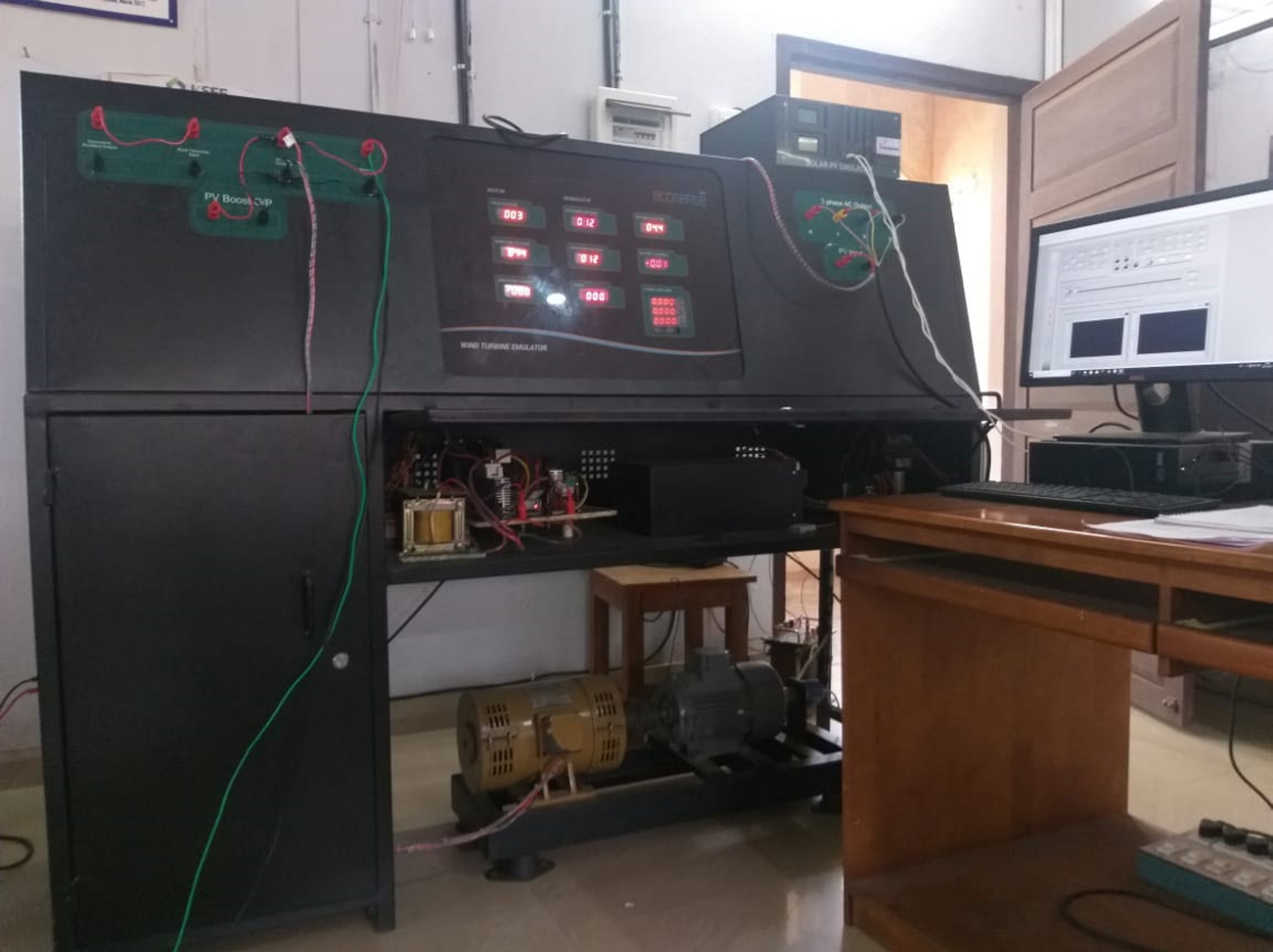

Photo of the complete microgrid system
These two system have been combined to get different combination of sources and with the grid through inverter.
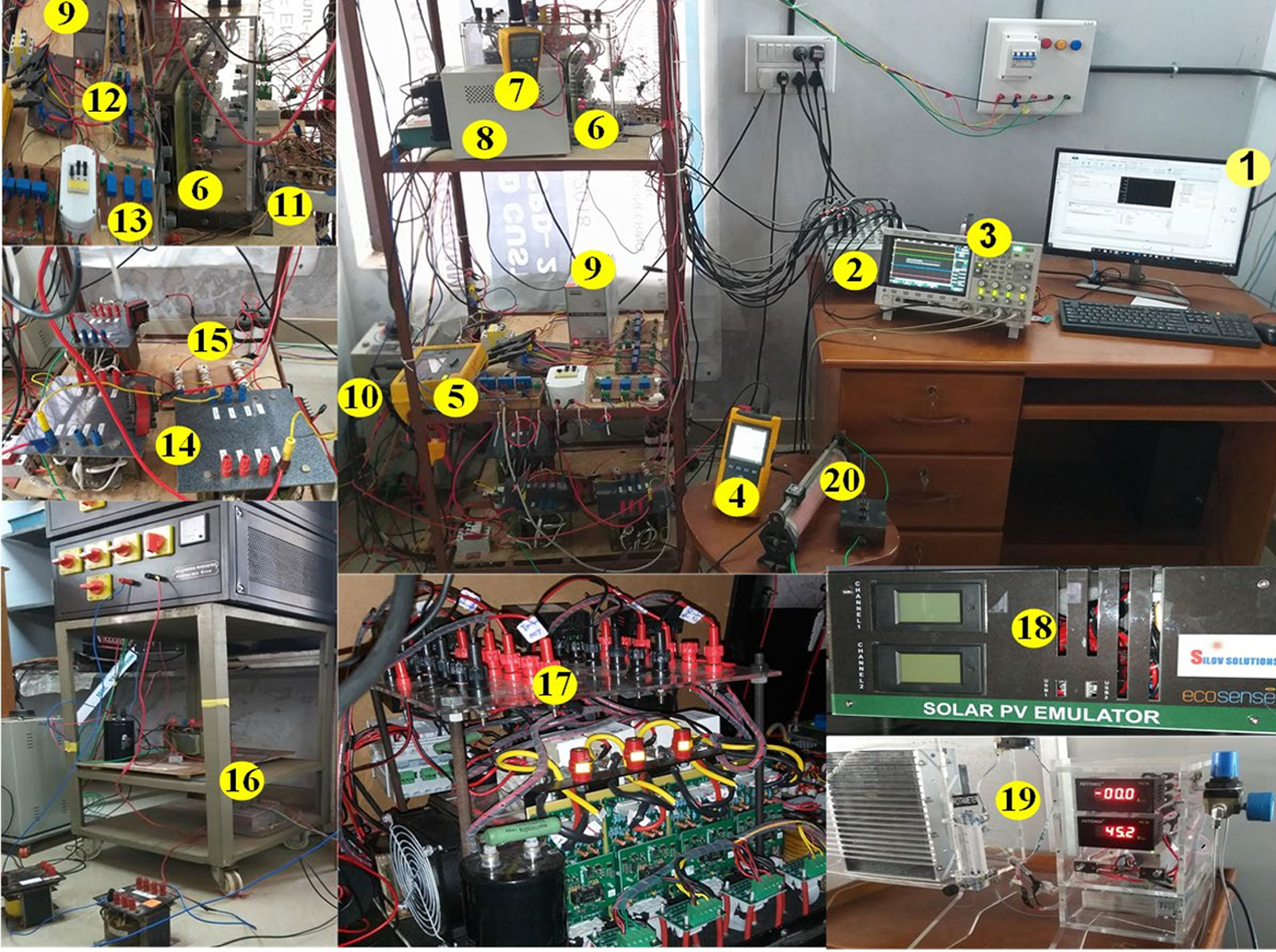
Experimental setup of a PV – Fuel Cell – Elctrolyser based hybrid system using three phase inverter - 1. Computer for hosting dSPACE software 2. dSPACE MicroLabBox 3. DSO 4. Power Quality Analyser 5. Power Logger 6. 3Φ voltage source inverter 7. DC link measurement 8. DC supply for gate driver circuit 9. DC supply for sensors 10. 3Φ grid 11. Gate driver circuit 12. Current sensor 13. Voltage sensor 14. Interfacing inductor 15. RC filter 16. Non linear load 17. DC-DC converters 18. Solar PV Emulator 19. Fuel cell 20. Dump load (Electrolyser)
Similar to the three phase inverter, this single phase inveter was assembled using Semikron inverter module (single phase), LEM sensors (voltage and current measurement), 6N136 based gate drive, interfacing inductor and RC ripple filter.
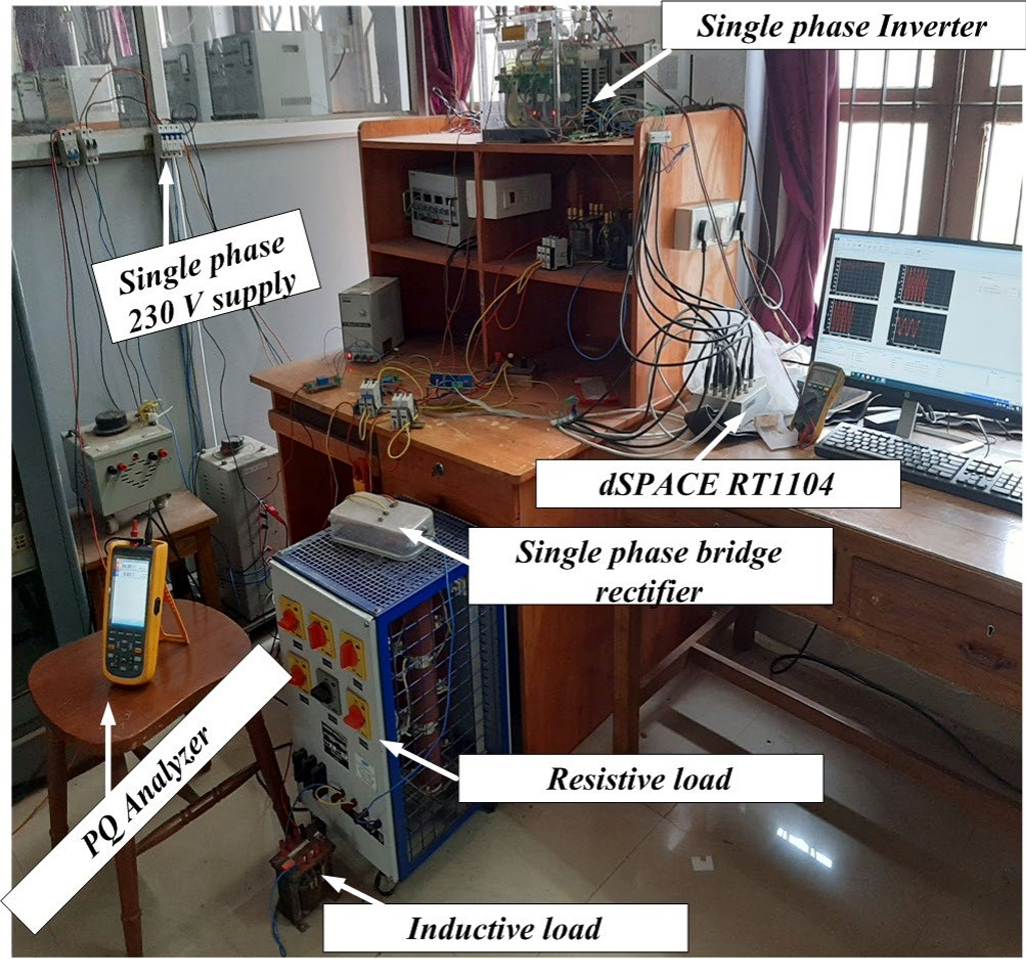
Photo of grid connected Single phase inverter
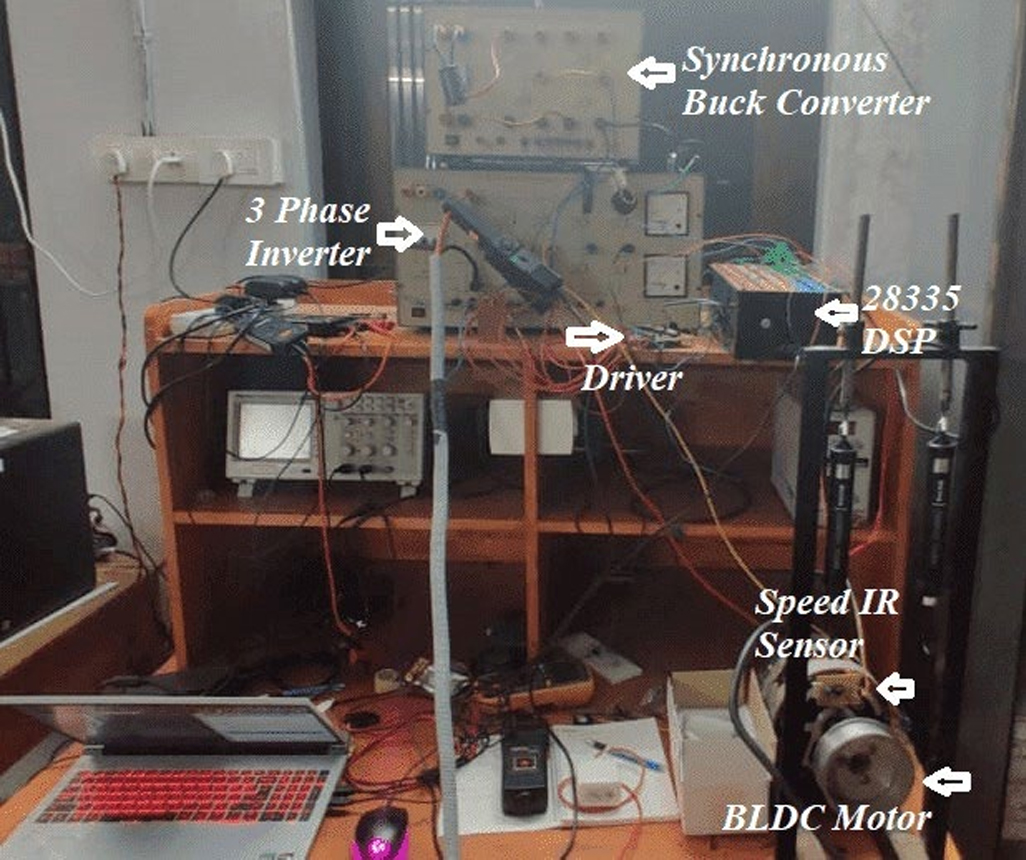
A BLDC motor sontrol sytem for a 1 kW motor was developed using battery bank, DC-DC converter and inverter. The system was controlled using a DSP controller (TMS320F28335).
| Academic Year | No. of first year Students intake in the year | No.of first year students admitted in the year | Academic Year | No. of students graduating in minimum stipulated time | No. of placed students | Medium salary of placed graduates (Amount in Rs.) | No. of students selected for higher studies |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019-2020 | 18 | 18 | 2020-2021 | 18 | 8 | 4.8 Lakhs/annum | 1 |
| 2020-2021 | 18 | 14 | 2021-2022 | 13 | 6 | 4.16 Lakhs/annum | 0 |
| 2021-2022 | 18 | 7 | 2022-2023 | 7 | 4 | 5.5 Lakhs/annum | 0 |